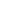
Activation of ALK triggers pathways involved in proliferation and
cell survival in normal physiology
Dimerisation
promotes ALK
autophosphorylation
2
3
Phosphate
group
P
P
Binding of the
ligands (the growth factors
MK or PTN) to ALK
induces dimerisation
2
2
MK or
PTN
Inside
Outside
Cell
membrane
ALK is a membrane-
bound protein
1
1
Activation
of signalling
pathways
MAPK
STAT3
PI3K/
AKT
Proliferation
Cell survival
Ligand-dependent activation
of downstream intracellular
signalling pathways
1,2
4
P
P
Inside
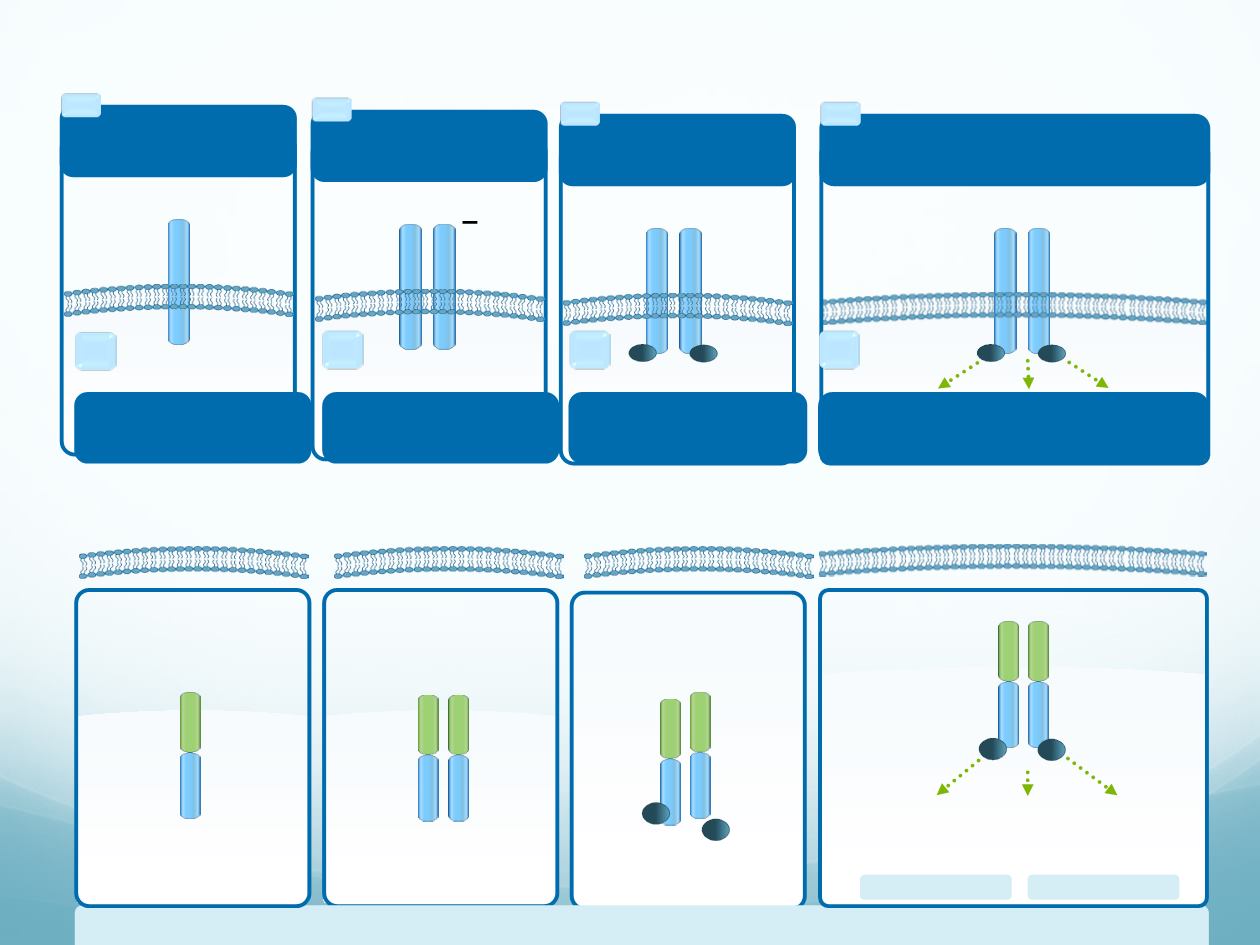
EML4-ALK activates signalling cascades in the
absence of ligand binding which promotes tumour growth
Activation
of signalling
pathways
MAPK
STAT3
PI3K/
AKT
EML4-ALK is
localised within
the cytoplasm
1
Independently of
ligand binding, EML4
mediates dimerisation
of EML4-ALK
2
EML4-ALK dimerisation
promotes EML4-ALK
autophosphorylation
2
1
3
2
EML4-ALK promotes tumour-cell growth and survival through the aberrant activation of pathways involved in
Proliferation
Cell survival
P
P
P
P
In the absence of ligand binding,
EML4-ALK is constitutively active
and activates intracellular
signalling cascades
1,2
4